1. Example: 단어 > 목록 변환¶
In [1]:
# sample 문장 입력
text = 'You say goodbye and I say hello.'
print (text)
In [2]:
# sample 문장을 모두 소문자로 변환 (대문자도 모두 소문자와 똑같이 취급하기 위해)
text = text.lower()
print (text)
In [3]:
# 마침표 앞에 공백 삽입
text = text.replace('.', ' .')
print (text)
In [4]:
# 공백을 기준으로 단어 분할
words = text.split(' ')
print(words)
2. 단어 목록 > 단어 ID 부여 & 단어와 짝짓기¶
In [5]:
word_to_id = {}
id_to_word = {}
for word in words:
if word not in word_to_id:
new_id = len(word_to_id) # 새로운 ID 부여
word_to_id[word] = new_id # 새로운 ID 할당
id_to_word[new_id] = word # 새로운 단어 할당
In [6]:
id_to_word
Out[6]:
In [7]:
word_to_id
Out[7]:
In [8]:
id_to_word[2]
Out[8]:
In [9]:
word_to_id['hello']
Out[9]:
In [10]:
# 단어 목록을 단어 ID 목록으로 변경
import numpy as np
corpus = [word_to_id[w] for w in words]
corpus = np.array(corpus)
corpus
Out[10]:
In [11]:
# 함수 만들어서 자동화 하기
def preprocess(text):
text = text.lower()
text = text.replace('.', ' .')
words = text.split(' ')
word_to_id = {}
id_to_word = {}
for word in words:
if word not in word_to_id:
new_id = len(word_to_id) # 새로운 ID 부여
word_to_id[word] = new_id # 새로운 ID 할당
id_to_word[new_id] = word # 새로운 단어 할당
corpus = [word_to_id[w] for w in words]
return corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word
In [12]:
text = 'You say goodbye and I say hello.'
corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word = preprocess(text)
In [13]:
print(corpus)
print(word_to_id)
print(id_to_word)
3. 단어의 동시발생행렬(co-occurrence matrix) 생성¶
In [14]:
def create_co_matrix(corpus, vocab_size, window_size = 1):
corpus_size = len(corpus)
co_matrix = np.zeros((vocab_size, vocab_size), dtype = np.int32)
for idx, word_id in enumerate(corpus):
for i in range(1, window_size + 1):
left_idx = idx - i
right_idx = idx + i
if left_idx >= 0:
left_word_id = corpus[left_idx]
co_matrix[word_id, left_word_id] += 1
if right_idx < corpus_size:
right_word_id = corpus[right_idx]
co_matrix[word_id, right_word_id] += 1
return co_matrix
In [15]:
co_matrix = create_co_matrix(corpus, len(corpus), 1)
print(co_matrix)
In [16]:
# 동시발생행렬 확인하기
import pandas as pd
co_temp = pd.DataFrame(co_matrix, columns = [words], index = [words])
In [17]:
co_temp
Out[17]:
4. 벡터 간 유사도¶
In [18]:
# 코사인 유사도: 두 단어 벡터의 가리키는 방향이 얼마나 비슷한가( 1 vs. -1)
def cos_similarity(x, y, eps=1e-8):
# 0 인 값이 들어오는 경우 에러를 방지하기 위한 작은 값 eps
nx = x / (np.sqrt(np.sum(x ** 2)) + eps)
ny = y / (np.sqrt(np.sum(y ** 2)) + eps)
return np.dot(nx, ny)
In [19]:
# you 와 i 의 유사도 확인
C0 = co_matrix[word_to_id['you']]
C1 = co_matrix[word_to_id['i']]
print(cos_similarity(C0, C1))
5. 유사 단어의 랭킹 표시¶
In [20]:
def most_simliar(query, word_to_id, id_to_word, co_matrix, top = 5):
# 검색어(query) 확인
if query not in word_to_id:
print('%s(을)를 찾을 수 없습니다.' % query)
return
print('\n[query] ' + query)
query_id = word_to_id[query]
query_vec = co_matrix[query_id]
# 단어 유사도 계산
vocab_size = len(id_to_word)
similarity = np.zeros(vocab_size)
for i in range(vocab_size):
similarity[i] = cos_similarity(co_matrix[i], query_vec)
# 계산된 유사도를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
count = 0
for i in (-1 * similarity).argsort():
# argsort: array 값을 오름차순으로 정렬하는 함수
if id_to_word[i] == query:
continue
print(' %s: %s' % (id_to_word[i], similarity[i]))
count += 1
if count >= top:
return
In [21]:
most_simliar('you', word_to_id, id_to_word, co_matrix, top = 5)
6. Word2Vec¶
In [22]:
# Matrix Multiply: MatMul을 이용한 역전파 계산
class MatMul:
def __init__(self, W):
self.params = [W]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(W)]
self.x = None
def forward(self, x):
W, = self.params
out = np.matmul(x, W)
self.x = x
return out
def backward(self, dout):
W, = self.params
dx = np.matmul(dout, W.T)
dW = np.matmul(self.x.T, dout)
self.grads[0][...] = dW
return dx
In [23]:
# 간단한 1행 array 데이터를 변환하여 가중치 곱 후 은닉층 전환 예시 (ppt p.38 아키텍처)
C = np.array([[1,0,0,0,0,0,0]])
W = np.random.randn(7,3)
layer = MatMul(W)
h = layer.forward(C)
print(h)
In [24]:
# CBOW 모델을 이용한 you 와 goodbye 추론 예시
# One-hot encoding
from numpy import array
from numpy import argmax
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
# define example
words = text.lower().replace('.', ' .').split(' ')
#print(words)
# integer encode
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
integer_encoded = np.sort(label_encoder.fit_transform(words))
#print(integer_encoded)
# binary encode
onehot_encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
integer_encoded = integer_encoded.reshape(len(integer_encoded), 1)
onehot_encoded = onehot_encoder.fit_transform(integer_encoded)
print(onehot_encoded)
CBOW Architecture Concept¶
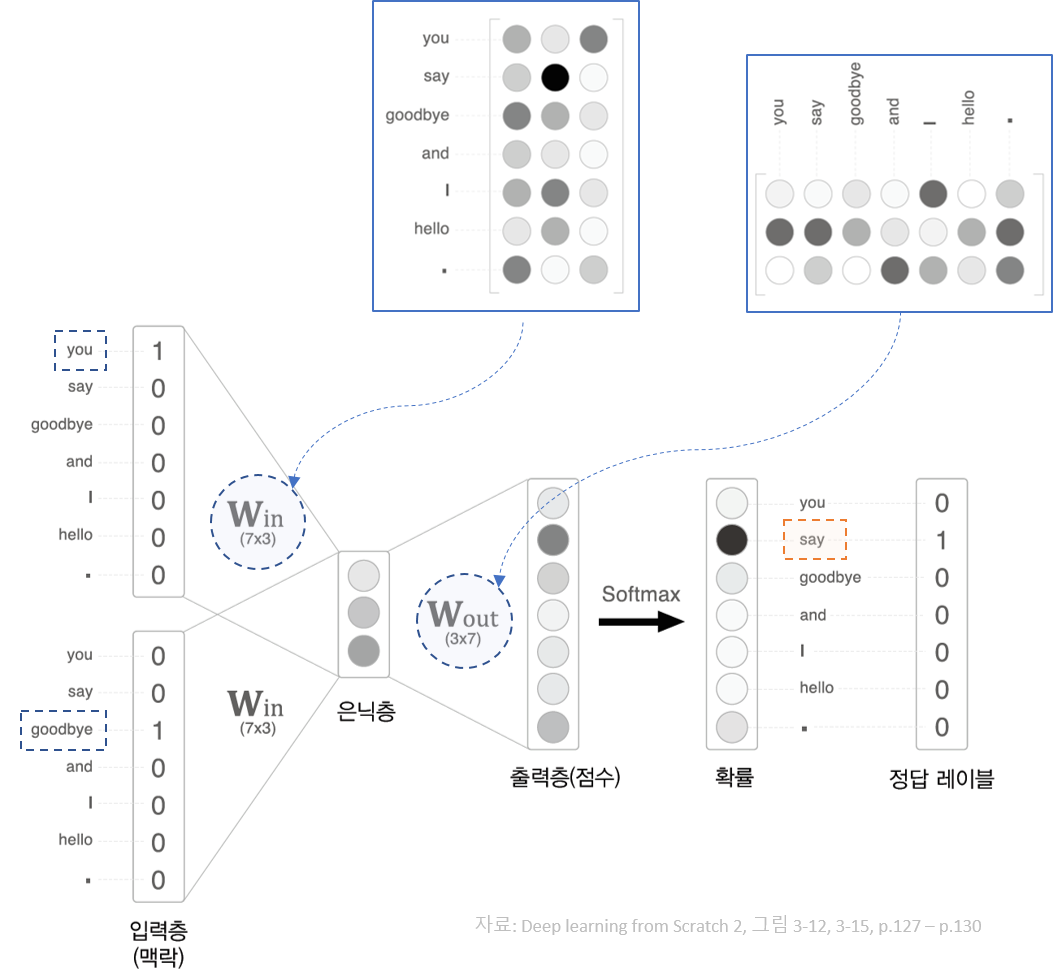
In [25]:
# 샘플 맥락 데이터
C0 = onehot_encoded[words.index('you'), :]
C1 = onehot_encoded[words.index('goodbye'), :]
# 가중치 초기화
W_in = np.random.randn(len(id_to_word), 3)
W_out = np.random.randn(3, len(id_to_word))
# 계층 생성
in_layer0 = MatMul(W_in)
in_layer1 = MatMul(W_in)
out_layer = MatMul(W_out)
# 순전파
h0 = in_layer0.forward(C0)
h1 = in_layer1.forward(C1)
h = 0.5 * (h0 + h1)
# 점수계산
s = out_layer.forward(h)
print(s)
말뭉치에서 맥락과 타깃을 만드는 예¶

In [26]:
# 말뭉치로부터 맥락과 타깃을 만드는 과정
corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word = preprocess(text)
print(corpus)
print(id_to_word)
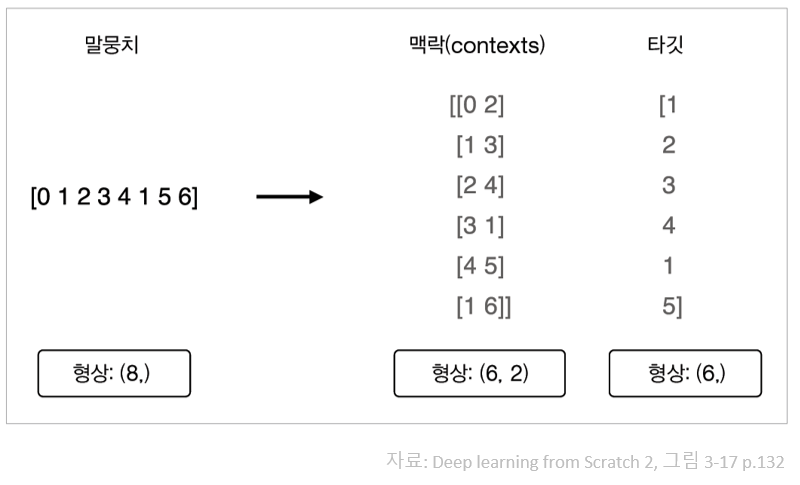
In [27]:
def create_contexts_target(corpus, window_size=1):
target = corpus[window_size:-window_size]
contexts = []
for idx in range(window_size, len(corpus)-window_size):
cs = []
for t in range(-window_size, window_size + 1):
if t==0:
continue
cs.append(corpus[idx + t])
contexts.append(cs)
return np.array(contexts), np.array(target)
In [28]:
contexts, target = create_contexts_target(corpus, window_size = 1)
print(corpus)
print(contexts)
print(target)
In [29]:
def convert_one_hot(corpus, vocab_size):
'''원핫 표현으로 변환
:param corpus: 단어 ID 목록(1차원 또는 2차원 넘파이 배열)
:param vocab_size: 어휘 수
:return: 원핫 표현(2차원 또는 3차원 넘파이 배열)
'''
N = corpus.shape[0]
if corpus.ndim == 1:
one_hot = np.zeros((N, vocab_size), dtype=np.int32)
for idx, word_id in enumerate(corpus):
one_hot[idx, word_id] = 1
elif corpus.ndim == 2:
C = corpus.shape[1]
one_hot = np.zeros((N, C, vocab_size), dtype=np.int32)
for idx_0, word_ids in enumerate(corpus):
for idx_1, word_id in enumerate(word_ids):
one_hot[idx_0, idx_1, word_id] = 1
return one_hot
vocab_size = len(word_to_id)
target = convert_one_hot(target, vocab_size)
contexts = convert_one_hot(contexts, vocab_size)
In [30]:
print(contexts)
In [31]:
print(target)
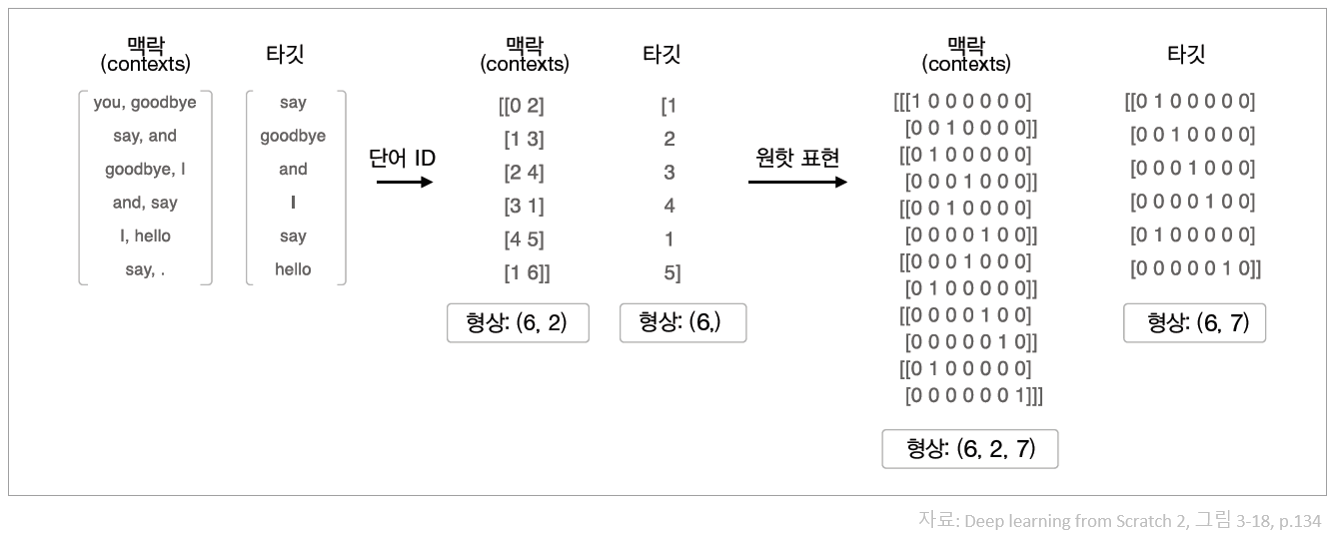
Word2Vec: CBOW model¶
CBOW architecture¶
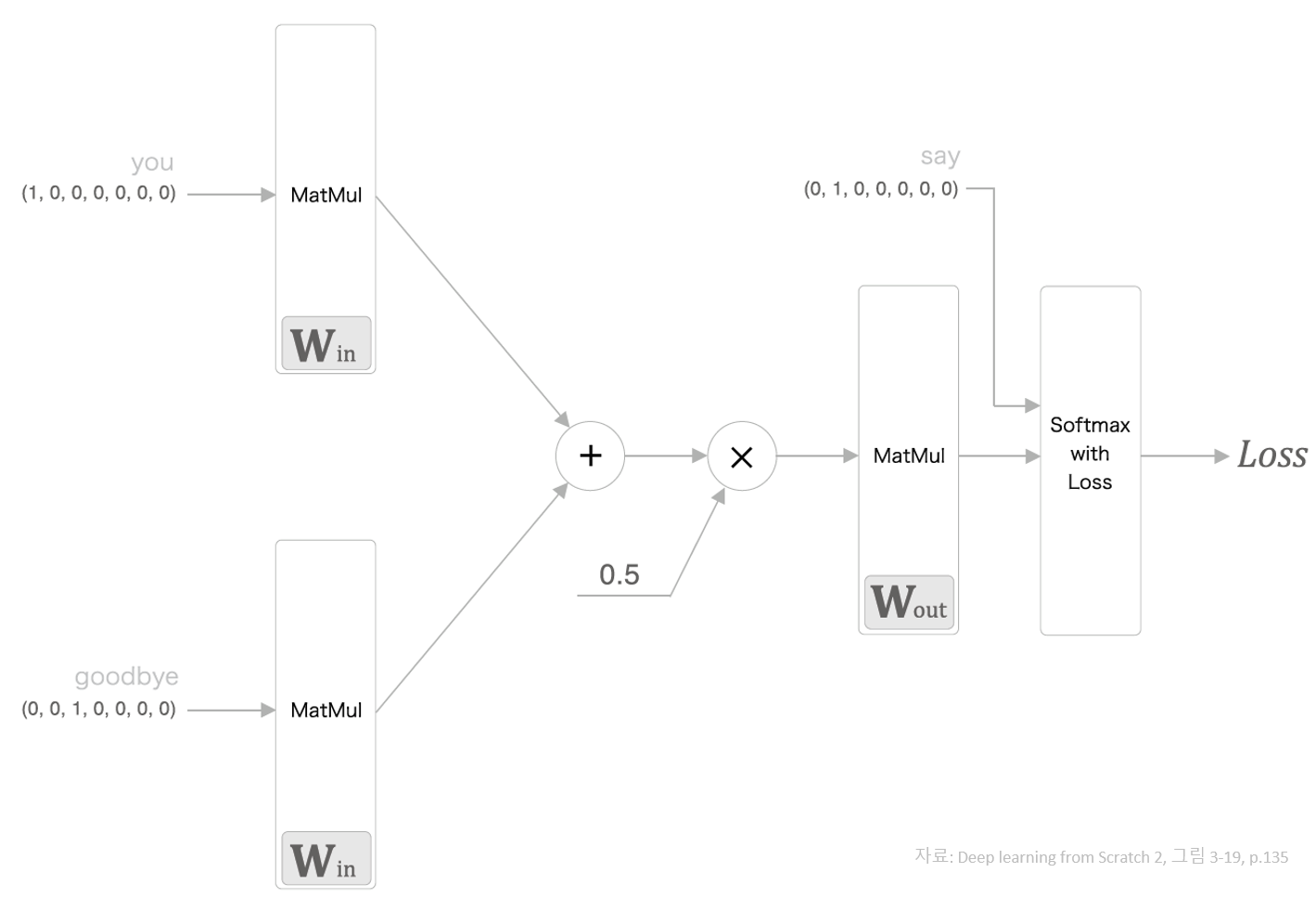
In [32]:
import time
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class SimpleCBOW:
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size):
V, H = vocab_size, hidden_size
# 가중치 초기화
W_in = 0.01 * np.random.randn(V, H).astype('f')
W_out = 0.01 * np.random.randn(H, V).astype('f')
# 계층 생성
self.in_layer0 = MatMul(W_in)
self.in_layer1 = MatMul(W_in)
self.out_layer = MatMul(W_out)
self.loss_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
# 모든 가중치와 기울기를 리스트에 모은다.
layers = [self.in_layer0, self.in_layer1, self.out_layer]
self.params, self.grads = [], []
for layer in layers:
self.params += layer.params
self.grads += layer.grads
# 인스턴스 변수에 단어의 분산 표현을 저장한다.
self.word_vecs = W_in
def forward(self, contexts, target):
h0 = self.in_layer0.forward(contexts[:, 0])
h1 = self.in_layer1.forward(contexts[:, 1])
h = (h0 + h1) * 0.5
score = self.out_layer.forward(h)
loss = self.loss_layer.forward(score, target)
return loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
ds = self.loss_layer.backward(dout)
da = self.out_layer.backward(ds)
da *= 0.5
self.in_layer1.backward(da)
self.in_layer0.backward(da)
return None
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None # 손실
self.y = None # softmax의 출력
self.t = None # 정답 레이블(원-핫 벡터)
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout = 1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
return dx
class Adam:
'''
Adam (http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980v8)
'''
def __init__(self, lr=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999):
self.lr = lr
self.beta1 = beta1
self.beta2 = beta2
self.iter = 0
self.m = None
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.m is None:
self.m, self.v = [], []
for param in params:
self.m.append(np.zeros_like(param))
self.v.append(np.zeros_like(param))
self.iter += 1
lr_t = self.lr * np.sqrt(1.0 - self.beta2**self.iter) / (1.0 - self.beta1**self.iter)
for i in range(len(params)):
self.m[i] += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[i] - self.m[i])
self.v[i] += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[i]**2 - self.v[i])
params[i] -= lr_t * self.m[i] / (np.sqrt(self.v[i]) + 1e-7)
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1, t.size)
y = y.reshape(1, y.size)
# 정답 데이터가 원핫 벡터일 경우 정답 레이블 인덱스로 변환
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(axis=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x - x.max(axis=1, keepdims=True)
x = np.exp(x)
x /= x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
elif x.ndim == 1:
x = x - np.max(x)
x = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
return x
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
def clip_grads(grads, max_norm):
total_norm = 0
for grad in grads:
total_norm += np.sum(grad ** 2)
total_norm = np.sqrt(total_norm)
rate = max_norm / (total_norm + 1e-6)
if rate < 1:
for grad in grads:
grad *= rate
class Trainer:
def __init__(self, model, optimizer):
self.model = model
self.optimizer = optimizer
self.loss_list = []
self.eval_interval = None
self.current_epoch = 0
def fit(self, x, t, max_epoch=10, batch_size=32, max_grad=None, eval_interval=20):
data_size = len(x)
max_iters = data_size // batch_size
self.eval_interval = eval_interval
model, optimizer = self.model, self.optimizer
total_loss = 0
loss_count = 0
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
# 뒤섞기
idx = numpy.random.permutation(numpy.arange(data_size))
x = x[idx]
t = t[idx]
for iters in range(max_iters):
batch_x = x[iters*batch_size:(iters+1)*batch_size]
batch_t = t[iters*batch_size:(iters+1)*batch_size]
# 기울기 구해 매개변수 갱신
loss = model.forward(batch_x, batch_t)
model.backward()
params, grads = remove_duplicate(model.params, model.grads) # 공유된 가중치를 하나로 모음
if max_grad is not None:
clip_grads(grads, max_grad)
optimizer.update(params, grads)
total_loss += loss
loss_count += 1
# 평가
if (eval_interval is not None) and (iters % eval_interval) == 0:
avg_loss = total_loss / loss_count
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
print('| 에폭 %d | 반복 %d / %d | 시간 %d[s] | 손실 %.2f'
% (self.current_epoch + 1, iters + 1, max_iters, elapsed_time, avg_loss))
self.loss_list.append(float(avg_loss))
total_loss, loss_count = 0, 0
self.current_epoch += 1
def plot(self, ylim=None):
x = numpy.arange(len(self.loss_list))
if ylim is not None:
plt.ylim(*ylim)
plt.plot(x, self.loss_list, label='train')
plt.xlabel('iterations (x' + str(self.eval_interval) + ')')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.show()
def remove_duplicate(params, grads):
'''
매개변수 배열 중 중복되는 가중치를 하나로 모아
그 가중치에 대응하는 기울기를 더한다.
'''
params, grads = params[:], grads[:] # copy list
while True:
find_flg = False
L = len(params)
for i in range(0, L - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, L):
# 가중치 공유 시
if params[i] is params[j]:
grads[i] += grads[j] # 경사를 더함
find_flg = True
params.pop(j)
grads.pop(j)
# 가중치를 전치행렬로 공유하는 경우(weight tying)
elif params[i].ndim == 2 and params[j].ndim == 2 and \
params[i].T.shape == params[j].shape and np.all(params[i].T == params[j]):
grads[i] += grads[j].T
find_flg = True
params.pop(j)
grads.pop(j)
if find_flg: break
if find_flg: break
if not find_flg: break
return params, grads
In [33]:
window_size = 1
hidden_size = 5
batch_size = 3
max_epoch = 1000
text = 'You say goodbye and I say hello.'
corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word = preprocess(text)
vocab_size = len(word_to_id)
contexts, target = create_contexts_target(corpus, window_size)
target = convert_one_hot(target, vocab_size)
contexts = convert_one_hot(contexts, vocab_size)
model = SimpleCBOW(vocab_size, hidden_size)
optimizer = Adam()
trainer = Trainer(model, optimizer)
trainer.fit(contexts, target, max_epoch, batch_size)
trainer.plot()